Contact: +91-9711224068

FAUNA
- Printed Journal
- Indexed Journal
- Refereed Journal
- Peer Reviewed Journal
Impact Factor: RJIF 5.53
e-ISSN : 2347-2677, p-ISSN : 2394-0522

International Journal of Fauna and Biological Studies
2016, Vol. 3 Issue 3, Part A
Diversity of larvivorous fish fauna in Lake Kolleru (AP), India
Author(s):
CH Krishna, J Chandra Sekhara Rao, K Veeraiah
Abstract:
Fish that are predatorsrnof the immature stages of mosquitoes are referred to as larvivorous larvivorous larvivorous larvivorous fish from 6 orders, 14rnfamilies and 20 genera. Order mugiliformes was the most dominant group with 9rnspecies and cyprinidae was the dominant family with 8 species. According to thernIUCN (2015) red list of threatened species, 89.65% of species are at leastrnconcern, 3.44% are at near threatened, 3.44% are not assessed and for 3.44% ofrnspecies data is deficient. As per the CAMP report (1998), 10 species are atrnlower risk near threatened, 1 at lower risk least concern, 5 are vulnerable, 12rnare not evaluated and for 1 species data is deficient. Out of 29 larvivorous from freshwaterrnregion only. Several anthropogenic activities including pollution, habitatrnloss, human interference, over exploitation and siltation are causingrnbiodiversity loss and seriously affecting the lake resources. The indigenousrnlarvivorous fish species of the lake can be successfully used for integratedrnvector control management.
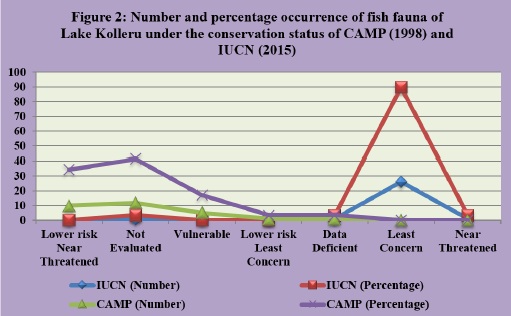
Fig. 1: Number and percent composition of families, genera and species under various orders
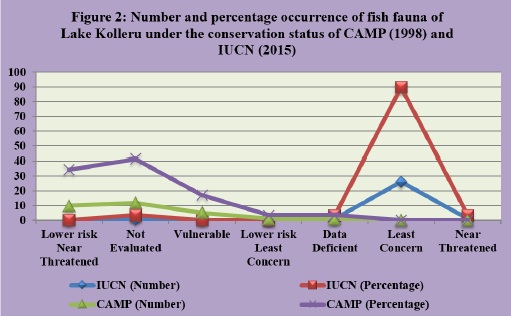
Fig. 2: Number and percentage occurrence of fish fauna of Lake Kolleru under the conservation status CAMP, 1998 and IUCN, 2013.jpg
Pages: 24-28 | 2291 Views 448 Downloads

How to cite this article:
CH Krishna, J Chandra Sekhara Rao, K Veeraiah. Diversity of larvivorous fish fauna in Lake Kolleru (AP), India. Int. J. Fauna Biol. Stud. 2016;3(3):24-28.
Important Publications Links
Related Journal Subscription
Allied Journals
Copyright © 2013 - 2024. All Rights Reserved. International Journal of Fauna and Biological Studies




